3D printing is an efficient method for producing small parts with intricate geometry. It offers precise and customizable solutions for various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical.
With the ability to create intricate designs, 3D printing allows for complex small parts that may not be achievable through traditional manufacturing methods.
Its cost-effectiveness and quick turnaround make it a viable option for rapid prototyping and production of small parts.
Additionally, 3D printing minimizes material waste and allows for design optimization, making it a versatile technology for small-part production.
Its potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes and deliver tailor-made solutions for specific applications has made 3D printing an attractive option for small parts production.
Understanding Small Parts 3d Printing
1. Advantages Of 3d Printing For Small Parts
Small parts 3D printing offers a plethora of benefits that conventional manufacturing methods often struggle to match.
The advantages of utilizing 3D printing technology for small parts are diverse and impactful, making it a highly desirable method for manufacturers.
2. Cost-effectiveness
3D printing small parts can result in cost savings due to the elimination of tooling and the ability to produce complex parts in a single manufacturing run.
This reduces the labor, material, and time costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
3. Customization Options
One of the most advantageous aspects of 3D printing for small parts is the level of customization it offers.
Manufacturers can create highly tailored, unique components without incurring additional tooling or machining costs, enabling them to produce personalized small parts at a competitive pace and cost.
4. Key Considerations For Small Parts 3d Printing
When engaging in small-parts 3D printing, several key considerations must be taken into account to ensure optimal results.
Among these considerations, material selection and precision requirements are of utmost importance.
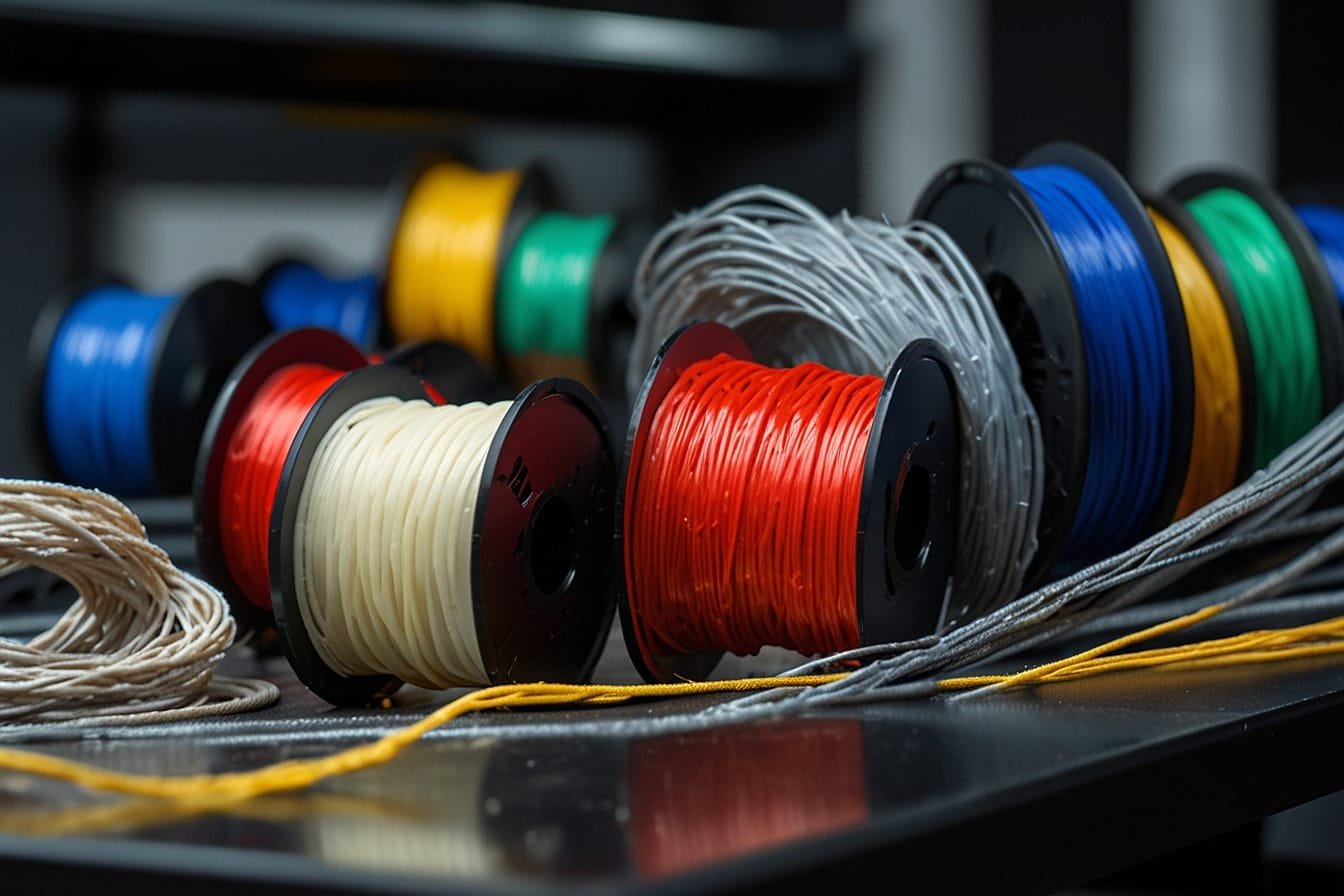
5. Material Selection
The selection of materials for small parts of 3D printing is critical to achieving the desired properties and performance of the components.
Factors such as strength, durability, and temperature resistance must carefully align with the specific application of the small part.
6. Precision Requirements
3D printing small parts demand a high level of precision to meet the functional specifications of the components.
Manufacturers must carefully assess the dimensional accuracy and surface finish requirements to ensure the printed small parts meet the desired standards.
Choosing The Right 3d Printing Technology
When it comes to 3D printing small parts, choosing the right 3D printing technology is essential for achieving optimal results.
Selecting the best 3D printing method for small parts will depend on factors such as precision, material compatibility, and production volume.
In this article, we will explore two popular 3D printing technologies for small parts – Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA), and discuss their advantages and suitability for precision production.
1. Overview Of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Technology
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a widely used 3D printing technology that operates by extruding thermoplastic material layer by layer to create the final 3D object.
FDM printers are known for their versatility and cost-effectiveness, making them popular for small-part production.
The technology allows for the use of a variety of materials, including ABS, PLA, PETG, and more, offering flexibility in material selection based on the specific requirements of the small parts.
2. The Advantages Of Stereolithography (SLA) For Precision Production
Stereolithography (SLA) is a resin-based 3D printing technology known for its exceptional precision and surface finish.
SLA printers utilize photopolymer resins that are cured layer by layer using a UV laser, resulting in high-resolution and detailed small parts with smooth surfaces.
This makes SLA ideal for applications where precision and intricate details are critical, such as jewelry, dental models, and prototyping of small mechanical parts.
Optimizing Design For Small Parts 3d Printing
Small parts 3D printing presents unique challenges and opportunities for designers.
Optimizing the design for small parts of 3D printing involves understanding the specific considerations required to achieve precision, accuracy, and successful print outcomes.
By addressing design, precision, and complexity, businesses can create small parts with exceptional quality, reliability, and functionality.
1. Design Considerations For Precision And Accuracy
Designing small parts for 3D printing requires careful consideration for achieving precision and accuracy.
Utilizing advanced CAD software and understanding the limitations of 3D printing technology is crucial for achieving precise and accurate small parts.
Dimensional accuracy, tolerances, and material selection play a critical role in optimizing the design for small parts of 3D printing.
Ensuring that the design is tailored to accommodate the printing process is essential for achieving the desired precision and accuracy.
2. Complex Geometries
Small parts often feature intricate and complex geometries that can be challenging to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
3D printing technology allows for the creation of complex geometries that may be impossible or cost-prohibitive with conventional manufacturing techniques.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of the 3D printing process is crucial for optimizing the design of small parts with complex geometries.
Utilizing support structures and proper orientation during printing is essential for achieving the desired geometries with high precision and quality.
3. Support Structure Optimization
Optimizing support structures is essential for successful small-parts 3D printing.
Proper placement and design of support structures are crucial for achieving accurate and high-quality prints.
Designers must consider the balance between sufficient support and minimizing post-processing efforts.
Utilizing advanced slicing software and optimizing print orientation is key to achieving efficient and effective support structures for small-parts 3D printing.
Quality Control And Finishing Techniques
Quality Control and Finishing Techniques play a crucial role in ensuring the functionality and aesthetics of small parts produced through 3D printing.
Post-processing procedures, such as surface smoothing and dimensional accuracy checks, are essential in refining the quality of small 3D printed parts.
In this section, we will explore the importance of post-processing and the various techniques involved in achieving impeccable results.
1. Post-processing For Small 3d Printed Parts
Post-processing for small 3D printed parts involves a series of meticulous steps aimed at enhancing the surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall quality of the components.
This phase is essential in refining the parts to meet the desired specifications and performance standards.
2. Surface Smoothing
Surface smoothing is a critical aspect of post-processing for small 3D printed parts.
It entails the application of smoothing techniques to eliminate layer lines and achieve a uniform, polished surface.
Techniques such as sanding, chemical smoothing, and vapor polishing are commonly employed to enhance the visual appeal and tactile feel of the printed parts.
3. Dimensional Accuracy Checks
Ensuring the dimensional accuracy of small 3D printed parts is imperative for their functionality and applicability in various industries.
Post-processing involves meticulous dimensional checks using precision instruments to verify the exactness of critical dimensions, tolerances, and overall geometry.
This step is instrumental in guaranteeing that the printed parts conform to the intended specifications.
Future Trends In Small Parts 3d Printing
As small parts 3D printing continues to evolve, future trends in this technology are poised to revolutionize various industries. From increasing automation and integration to industry-specific applications, these advancements are set to impact the manufacturing landscape significantly.
1. Automation And Integration
The future of small parts 3D printing lies in the increased need for automation and seamless integration into existing manufacturing processes.
Advanced robotic systems and AI algorithms are being developed to streamline the entire 3D printing workflow, from design to production, ensuring efficiency and precision.
The integration of automated quality control measures will also become prevalent, leading to higher reliability and consistency in small parts production.
2. Industry-specific Applications
Small parts 3D printing is expected to find specific applications across various industries.
The medical sector is exploring this technology for customized implants and prosthetics, while the aerospace industry is utilizing it for lightweight components.
In the automotive field, small parts 3D printing is enabling the creation of complex, high-performance parts with enhanced functionality.
The ability to cater to industry-specific requirements will drive the widespread adoption of this technology.
Frequently Asked Questions For Small Parts 3d Printing
What Are The Benefits Of Small Parts 3d Printing?
Small parts 3D printing offers precision, customization, rapid prototyping, and cost-effectiveness for manufacturing components.
How Can Small Parts 3d Printing Improve Production Processes?
Utilizing small parts 3D printing can streamline production, reduce material waste, enable complex geometries, and enhance overall efficiency.
What Materials Can Be Used For Small Parts 3d Printing?
A wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, can be used in small parts of 3D printing processes.
Is Small Parts 3d Printing Suitable For Intricate Designs?
Yes, small-parts 3D printing excels at producing intricate and detailed designs with high accuracy and resolution.
Can Small Parts 3d Printing Reduce Production Lead Times?
Small parts 3D printing can significantly shorten production lead times compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Are Small Parts 3d Printed Components Durable?
Small parts 3D printed components can be highly durable, depending on the material and printing parameters used.
How Does Small Parts 3d Printing Impact Cost Savings?
Small parts 3D printing can minimize tooling costs, reduce material waste, and lower overall production expenses.
Can Small Parts 3d Printing Support Low-volume Production?
Yes, small-parts 3D printing is ideal for low-volume production runs, offering flexibility and scalability.
What Industries Can Benefit From Small Parts 3d Printing?
Various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer goods, can benefit from small parts 3D printing capabilities.
What Are The Design Considerations For Small Parts 3d Printing?
Design for manufacturability, support structures, and material selection are crucial considerations for small parts 3D printing success.
Conclusion On Small Parts 3d Printing
Innovations in small parts 3D printing offer numerous benefits for various industries.
The precision and efficiency of this technology provide cost-effective solutions for manufacturing intricate components.
Embracing small parts in 3D printing opens the door to limitless possibilities and drives the advancement of modern manufacturing.
Explore the potential of this transformative technology today.